Helium

Gas Factfile
Helium (He) is the second lightest process gas next to hydrogen.
Colorless, odorless, tasteless, nontoxic and chemically inert, helium is nonflammable and, when compared with argon, has a high thermal conductivity.
Helium-enhanced mixtures are utilized to create an inert gas shield and prevent oxidation during open arc welding of metals such as aluminum, stainless steel, copper and magnesium alloys.
The addition of helium generally increases weld pool fluidity and travel speed. Penetration properties will be broader and travel speed is typically increased with the addition of helium to the shielding gas mixture.
Use of helium-enhanced mixtures will also lessen the formation of welding ozone when welding on aluminum alloys.
| UN Number | 1046 |
| CAS Number | 7440-59-7 |
| EC Number | 231-168-5 |
| DOT Label | Non Flammable gas |
| Hazard labels required | ADR Class 2, 1A DOT Class 2.2 |
Where is it used ?
Helium is used in various applications. Here are some examples.
Medical
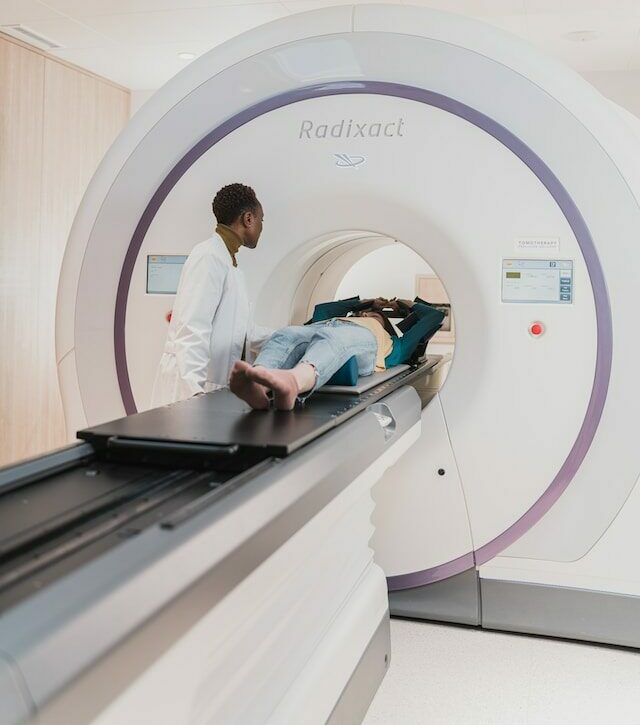
The largest single use of liquid helium is to cool the superconducting magnets in modern MRI scanners.
Welding
Used as a shielding gas in arc welding processes on materials that at welding temperatures are contaminated and weakened by air or nitrogen
Semiconductor
Used as a protective gas in growing silicon and germanium crystals, in titanium and zirconium production, and in gas chromatography.